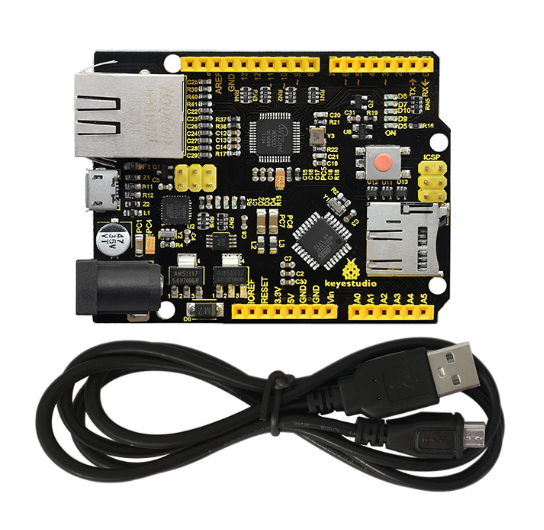
KS0304 Keyestudio W5500 Ethernet Geliştirme Kartı (POE'siz)

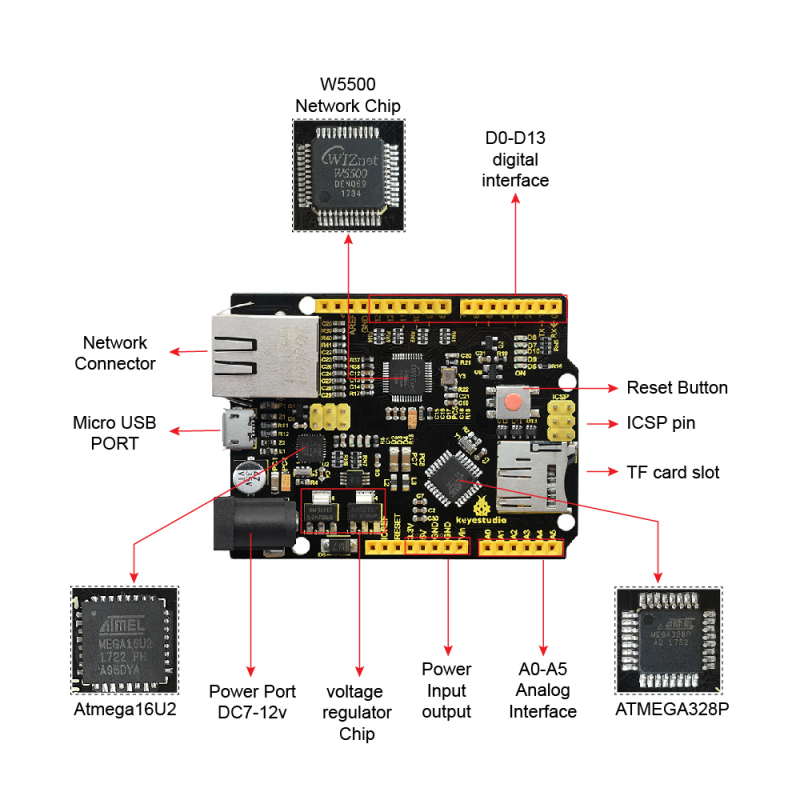
Arayüzler
Çip Hakkında:
- 1.ATMEGA328P-AU
- 2.Atmega16U2
- USB'den seri yongaya
- 3.AMS1117
- 4.5V ve 3.3V stabilivolt çip
- 5.W5500 ağ yongası
Arayüz Hakkında:
1. ICSP arayüzü
- Firmware'i ATMEGA328P-AU'ya programlayın
2. Dijital arayüz D0-D13
- Seri iletişim : D0 (RX) ve D1 (TX)
- Harici kesinti : D2 (kesinti 0) 、 D3 (kesinti 1)
- PWM arayüzü : D3 、 D5 、 D6 、 D9 、 D10 、 D11
- SPI iletişimi : D10 (SS) 、 D11 (MOSI) 、 D12 (MISO) 、 D13 (SCK)
3. ICSP arayüzü
- Aygıt yazılımını Atmega16U2'ye programlayın
4. USB girişi
- Program indirme veya seri hata ayıklama için
5. DC güç konektörü
- 7V-12V voltajına erişim
6. Güç çıkışı bağlantı noktası
- Harici güç kaynağı veya ortak toprak tutacağı için çıkış 3.3V veya 5V ,
7. Analog arayüz A0-A5
- IIC iletişimi : A4 (SDA) ve A5 (SCL)
- Ayrıca dijital arayüz olarak kullanılabilir : A0 (D14) 、 A1 (D15) 、 A2 (D16) 、 A3 (D17) 、 A4 (D18) 、 A5 (D19)
8. Ağ konektörü
- RJ - 45 ağ bağlantı noktası
Bileşen Hakkında:
- 1. sıfırlama düğmesi
- 2.16MHz kristal osilatör
- 3.25MHz kristal osilatör
Test Kodu
Aşağıda örnek bir kod var, kopyalayıp yapıştırabilirsiniz Arduino IDE.
#include |
Kod B:
//in testing, check IP address of reticle through GET_IP routine //for example, the tested IP address is 192.168.1.113 //namely intranet address allocated to testing reticle #include |
Test Adımları ve Sonuç
1. Test etmeden önce gerekli kitaplıkları IDE kitaplık dizinine yerleştirin.
2. İlk test için DC7-12V 、 USB MICRO 、 TF kartı ve ağ kablosunu bağlayın. Ağa erişim varsa, ağ başlığındaki iki LED yanıyor, D5 、 D7 、 D8 、 D9 、 D10 LED yanıyor ve D8 LED'i yanıp sönüyor.
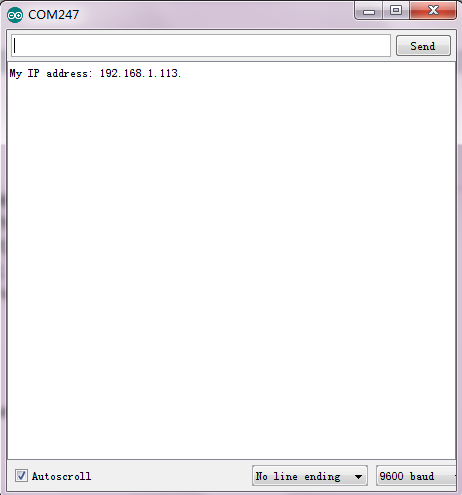
3. Ana kart üzerindeki A, D2 、 D3 、 D4 kodunu yükleyin ışığı yanar. Yükleme tamamlandı, seri monitörü açın, aşağıda gösterilen 192.168.1.113 ağ IP adresini görebilirsiniz.
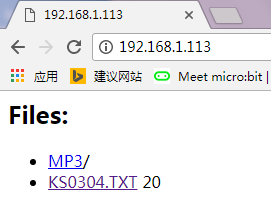
4. Ardından, B kodunu yükleyin, B kodunun IP adresi, A kodunun IP adresi olarak revize edilmelidir. Yükleme tamamlandı, tarayıcı adres çubuğuna aldığınız IP adresini girin, web sayfasında mevcut SD kart içeriğini gösterecektir. TXT dosyasıysa, içeriğini kontrol etmek için tıklayabilirsiniz. Aşağıda gösterilen.
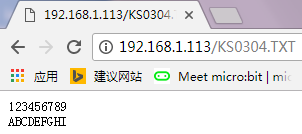
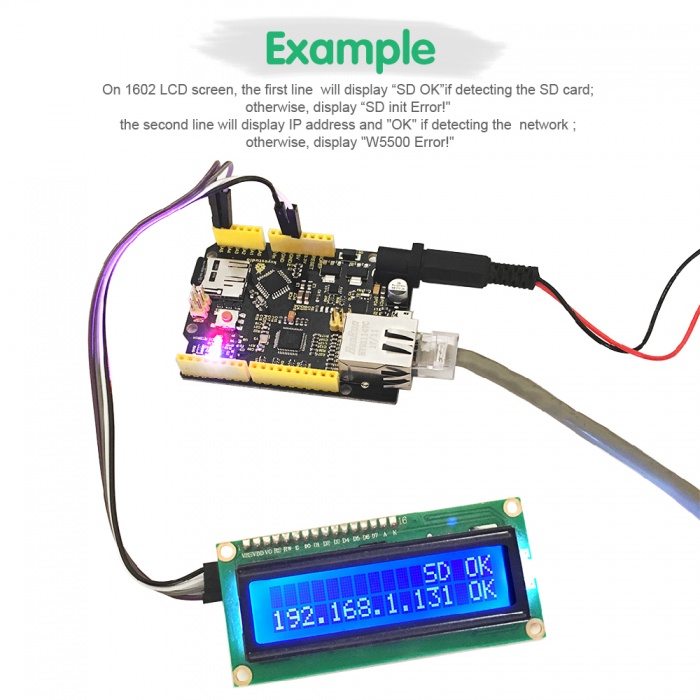
Örnek Gösteri
Kaynak
Test Kodu, Kitaplık:
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0304
Paket içeriği
- Keyestudio W5500 ethernet geliştirme kartı *1adet
- Siyah USB Kablo *1adet